Elevated Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide Predicts Impaired Vascular Reactivity in Patients with Hypertension
- Nov 25, 2025
- 1 min read
Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Sep 20;15(18):2400.
I-Min Su, Ji-Hung Wang, Chin-Hung Liu, Bang-Gee Hsu
Abstract
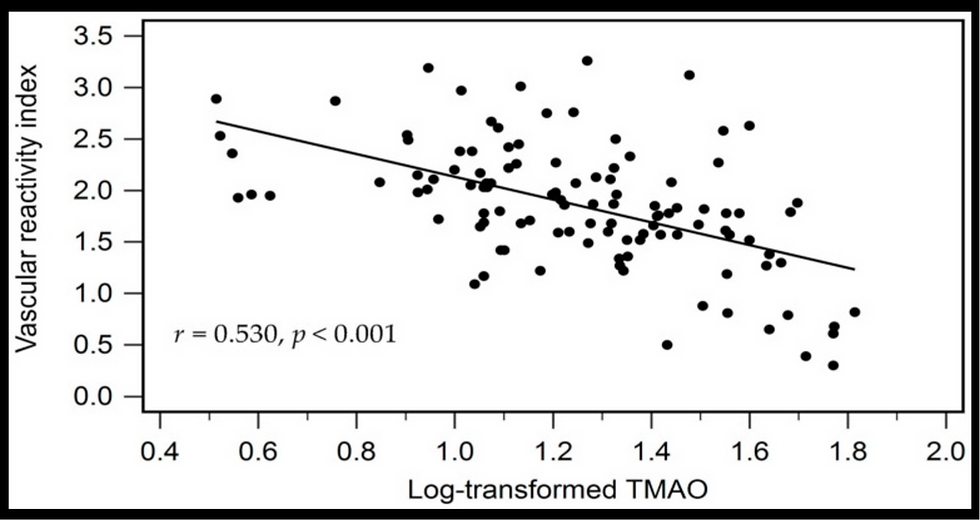
Background/Objectives: Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a gut microbiota-derived metabolite influenced by diet, has been linked to cardiovascular disease. Endothelial dysfunction, an early sign of vascular damage, is common in hypertension. This study examined the relationship between serum TMAO levels and endothelial function, assessed by the vascular reactivity index (VRI), in patients with hypertension. Methods: In total, 110 patients with hypertension were enrolled. Fasting serum TMAO was measured using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Endothelial function was evaluated via digital thermal monitoring, with VRI categorized as good (>2.0), intermediate (1.0-1.9), or poor (<1.0). Results: Of the participants, 10 (9.1%) exhibited poor vascular reactivity, 57 (51.8%) had intermediate reactivity, and 43 (39.1%) exhibited good vascular reactivity. Poor reactivity correlated with older age (p = 0.010), higher total cholesterol (p = 0.007), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (p = 0.009), and higher TMAO levels (p < 0.001). In multivariate forward stepwise linear regression, the log-transformed TMAO level (log-TMAO) remained independently and inversely associated with VRI (p < 0.001). Logistic regression analyses demonstrated that elevated TMAO concentrations were significantly associated with an increased likelihood of vascular reactivity dysfunction (intermediate and poor groups combined; odds ratio [OR] = 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.047-1.155; p < 0.001) and, in particular, with poor vascular reactivity (OR = 1.58, 95% CI: 1.002-2.492; p = 0.049).
Conclusions: Elevated serum TMAO is independently associated with endothelial dysfunction in hypertension.
Keywords: digital thermal monitoring; endothelial dysfunction; hypertension; trimethylamine N-oxide; vascular reactivity index.


Comments